How Fear Affects the Body: Understanding the Physical Impact
How fear affects the body is a question that touches everyone’s life at some point. Your heart pounds, your palms sweat, and your muscles tense—all within seconds of perceiving danger. These dramatic physical changes reveal a profound truth: your emotions directly shape your body’s responses. Fear doesn’t just live in your mind; it courses through every cell, nerve, and organ in your physical system.
This article explores the fascinating mechanisms behind fear’s physical effects. You’ll discover why your body reacts so powerfully to threats, whether sustained anxiety can lead to actual illness, and how emotional distress spreads between people. Most importantly, you’ll learn practical ways to reduce fear’s harmful impact on your wellbeing.
By understanding these connections, you’ll recognize fear’s physical signatures and respond more effectively when anxiety threatens your health.
How Fear Affects the Body: The Nervous System Response
Your nervous system orchestrates an immediate response when fear strikes. The sympathetic nervous system activates what scientists call the fight-or-flight response, preparing your body to confront danger or escape from it. This ancient survival mechanism happens automatically, without conscious thought.
Within milliseconds, your brain’s fear centers send urgent signals throughout your body. Stress hormones flood your bloodstream. Adrenaline surges first, followed by cortisol, creating a cascade of physical changes. Your heart rate jumps dramatically, sometimes doubling within seconds. Blood pressure rises as your cardiovascular system works harder.
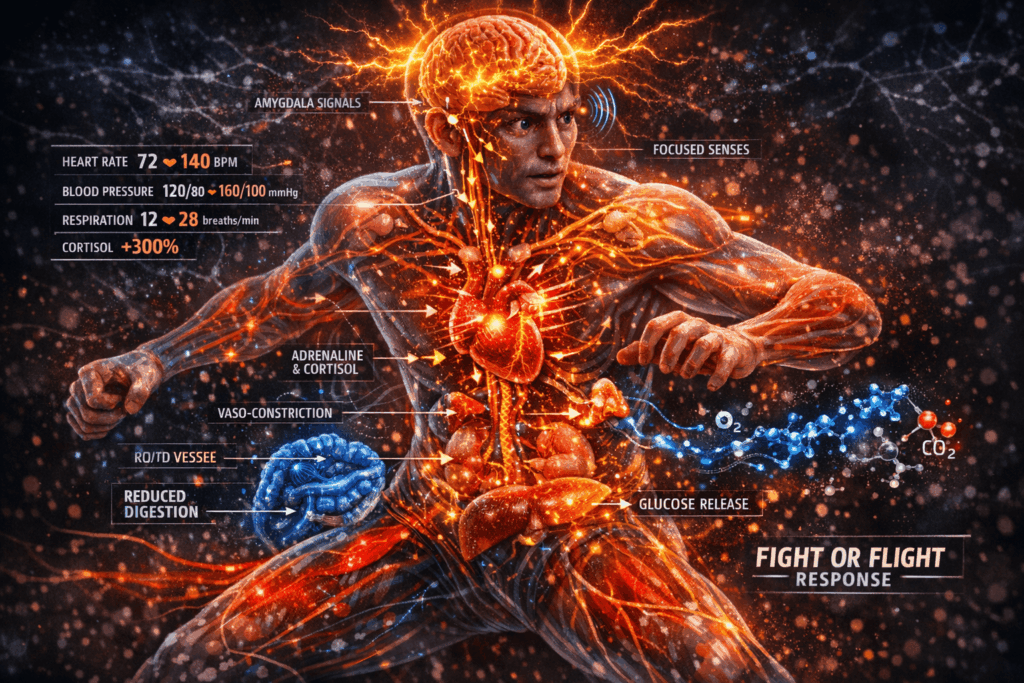
Your breathing pattern shifts immediately. Instead of slow, deep breaths, you take rapid, shallow gulps of air. This breathing change prepares your muscles for action but can create feelings of lightheadedness.
Blood flow redirects away from your digestive organs and toward your major muscle groups, explaining why fear often causes stomach discomfort.
Therefore, how fear affects the body demonstrates remarkable biological coordination. Your pupils dilate to sharpen vision. Your liver releases stored glucose, flooding your system with quick energy. Muscles throughout your body contract and tense, ready for explosive action. Understanding the mind-body connection and sickness helps explain why emotions create such powerful physical responses.
The vaso-motor nerves, which control blood vessel tightening and relaxation, play a critical role during fearful episodes. When fear paralyzes these nerve centers, it produces both muscular relaxation and capillary congestions throughout your system. As a result, you might experience unusual sensations like tingling, numbness, or waves of heat and cold.
Can Fear Cause Illness?
Can fear cause illness? Medical observations spanning centuries suggest that fear can indeed contribute to physical disease, though the relationship proves more complex than simple cause and effect. Short-term fear produces temporary changes that typically resolve quickly. However, chronic fear creates sustained stress that gradually weakens your body.
Historical medical records document numerous instances where intense fright produced immediate physical consequences. Physicians have recorded cases of sudden paralysis, severe nervous shock, and even fatal outcomes following extreme fear. One physician reported a striking case involving a patient who believed he had suffered a mortal injury. His fear became so overwhelming that his body entered a near-death state—circulation failing, temperature dropping, and vital signs collapsing. When the doctor proved no injury existed, the patient’s symptoms reversed almost instantly, demonstrating fear’s profound physiological power.
Because fear operates through concrete biological pathways, prolonged exposure can contribute to stress-related conditions. Chronic activation of stress hormones may compromise immune function and increase systemic inflammation. Consequently, sustained anxiety has been linked to cardiovascular problems, digestive disorders, and reduced resistance to infections.
Epidemic spread provides another revealing example of whether fear can cause illness. During outbreaks of cholera, smallpox, and diphtheria, medical observers noted that communities gripped by intense anxiety experienced higher infection rates. Fear itself appeared to weaken people’s natural resistance, making them more vulnerable to disease. This phenomenon demonstrates how emotional states directly influence physical health outcomes.
Effects of Fear on Physical Health
The effects of fear on physical health extend across multiple body systems. Recognizing these impacts helps you understand when emotional distress manifests physically.
Cardiovascular System: Fear dramatically increases heart rate and blood pressure. Your heart pounds harder and faster, pushing blood to your extremities. Over time, chronic anxiety may contribute to hypertension and increase strain on your cardiovascular system. The constant elevation of stress hormones can damage blood vessel linings and promote dangerous inflammation.
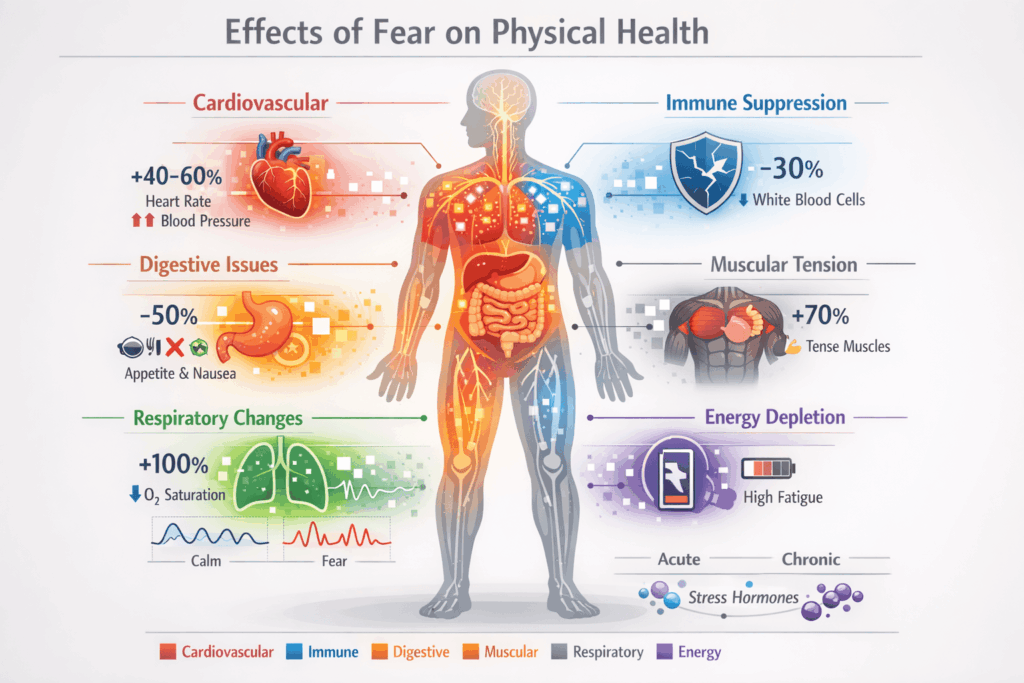
Immune Function: Sustained fear suppresses your body’s natural defenses. Cortisol, while helpful during brief stress, inhibits immune cell activity when present continuously. This suppression reduces your ability to fight infections and recover from illness. Research on fear and physical health confirms these immune system connections.
Digestive System: Fear redirects blood away from digestive organs, causing immediate discomfort. You might experience nausea, stomach pain, or appetite changes. Chronic fear can contribute to serious digestive disorders and nutrient absorption problems. Some people develop stress-related conditions that affect their entire gastrointestinal function.
Muscular Tension: Fear causes widespread muscle contraction throughout your body. Your shoulders rise, your jaw clenches, and your entire frame becomes rigid. Prolonged tension leads to muscle fatigue, chronic pain, and reduced flexibility. Many people carry this tension without realizing fear drives these physical symptoms. Learning about how emotions affect your body provides deeper insight into these connections.
Respiratory Changes: Rapid, shallow breathing during fearful episodes reduces oxygen delivery to tissues. This breathing pattern creates lightheadedness and may trigger additional anxiety. The effects of fear on physical health include this respiratory disruption, which can perpetuate the fear cycle.
Energy Depletion: Fear causes peculiar fatigue that extends beyond normal tiredness. Your body burns through energy reserves at an accelerated rate. This depletion leaves you feeling exhausted, even when you haven’t engaged in physical activity. The vitality drain from sustained fear can be profound and persistent.
Why Fear Feels Contagious
Fear possesses an unusual quality that sets it apart from other emotions: it spreads rapidly between people. When one person displays fear, others nearby often experience identical physical sensations. Their hair stands on end, chills run along their spines, and cold perspiration breaks out across their skin.
This contagious nature occurs because humans evolved for group survival. Your nervous system constantly scans others for danger signals. When someone near you exhibits fear—through facial expressions, body language, or vocal tones—your system automatically prepares to respond. This instant communication happens below conscious awareness.
Group fear dynamics create powerful cascading effects in communities. One person’s anxiety triggers responses in others, which amplifies the original fear and creates a feedback loop. Therefore, panic can sweep through crowds within moments. This explains why collective anxiety intensifies during uncertain times and why epidemics historically gained stronger footholds in frightened populations.
Under proper conditions, fear manifested by one individual instantly communicates to the entire group. People feel little chills running up and down their spines. Their hearts begin racing in unison. As a result, this shows the profound effect fear has on bodily functions and how easily anxiety spreads without rational cause.
Understanding this contagious quality helps explain why managing fear requires both individual awareness and supportive social environments. Exploring thought and consciousness reveals how mental patterns shape collective experiences.
Reducing the Harmful Effects of Fear
While some fear serves protective purposes, managing excessive anxiety protects your physical wellbeing. Several approaches can help reduce how fear affects the body negatively.
Trust and mental reframing provide powerful tools for overcoming fear’s paralytic effects. When you consciously cultivate confidence in your ability to handle challenges, you counter anxiety’s grip. This doesn’t mean ignoring real dangers, but rather approaching threats with measured confidence instead of overwhelming dread. Opening your mind to natural faith and trust creates a foundation for emotional stability.
Calm responses interrupt the fear cycle effectively. When you notice anxiety arising, deliberately slow your breathing. Take deep breaths that engage your diaphragm rather than quick chest breaths. This simple act signals your nervous system that immediate danger isn’t present, helping reverse the stress response. A determined opposition to fear, accompanied by trust and faith in your own powers, proves highly beneficial.
Mind-body balance practices support overall resilience against chronic stress. Activities like gentle movement, meditation, and spending time in nature help regulate nervous system activity. Understanding your body’s chakra system and energy provides additional framework for maintaining equilibrium.
Social support matters significantly in managing fear’s physical effects. Surrounding yourself with calm, reassuring people helps counter anxiety’s contagious nature. Trusted relationships provide emotional grounding during uncertain periods. For comprehensive guidance, this fear and health resource offers practical strategies.
Practical approaches should remain realistic and achievable. Reasoning helps you overcome momentary instinctive fear—the kind that flashes through your system and passes quickly. Conscious, reflective fear requires more sustained effort. An effort of will becomes necessary to banish fear from your mental domain permanently. Small, consistent practices work better than dramatic interventions for lasting change.
Conclusion
Understanding how fear affects the body empowers you to recognize and respond to its physical manifestations. Fear triggers immediate nervous system responses involving stress hormones, cardiovascular changes, and altered breathing patterns. While brief fear serves protective functions, chronic anxiety can compromise immune function, cardiovascular health, and overall wellbeing.
The effects of fear on physical health extend beyond individual experience—anxiety spreads between people and can weaken entire communities during stressful periods. However, cultivating trust, practicing calm responses, and maintaining mind-body awareness can reduce fear’s harmful impacts. Therefore, recognizing fear’s physical signatures and developing healthy coping strategies helps you maintain both emotional and physical health throughout life’s challenges. Your body truly reflects your emotional states, making peace of mind essential for lasting wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions: Understanding Fear and the Body
How does fear affect the body physically?
Fear affects the body by activating the fight-or-flight response, which increases heart rate, muscle tension, and stress hormone release. This response explains how fear affects the body in moments of perceived danger, but repeated activation can strain multiple body systems and disrupt normal function.
Can fear cause illness over time?
Yes, fear can cause illness when it becomes chronic. Prolonged exposure to stress hormones like cortisol may weaken the immune system, elevate blood pressure, and contribute to digestive and inflammatory conditions.
How does fear affect the body differently from other emotions?
Fear creates more intense physical responses than most emotions, clearly illustrating how fear affects the body at a survival level. It triggers rapid hormonal surges, widespread muscle tension, and measurable changes in heart rate and breathing patterns that other emotions do not typically produce.
How does prolonged anxiety affect digestion?
Prolonged anxiety disrupts normal digestive function and is one of the key effects of fear on physical health. Fear redirects blood away from digestive organs, slows digestion, and can cause nausea, stomach pain, or appetite changes over time.
How can I reduce fear’s negative effects on my body?
You can reduce fear’s effects through several approaches. Practice slow, deep breathing to calm your nervous system. Cultivate trust and positive mental frameworks. Engage in regular physical activity and maintain supportive social connections. These strategies help interrupt the fear cycle and promote resilience. Explore more from our article on mindful awareness for insights on how to practice deep breathing and living mindfully.
